Veterinary Orthoses for Dogs
Custom-designed orthotic devices to support, stabilize, and protect limbs for improved mobility and long-term musculoskeletal health.
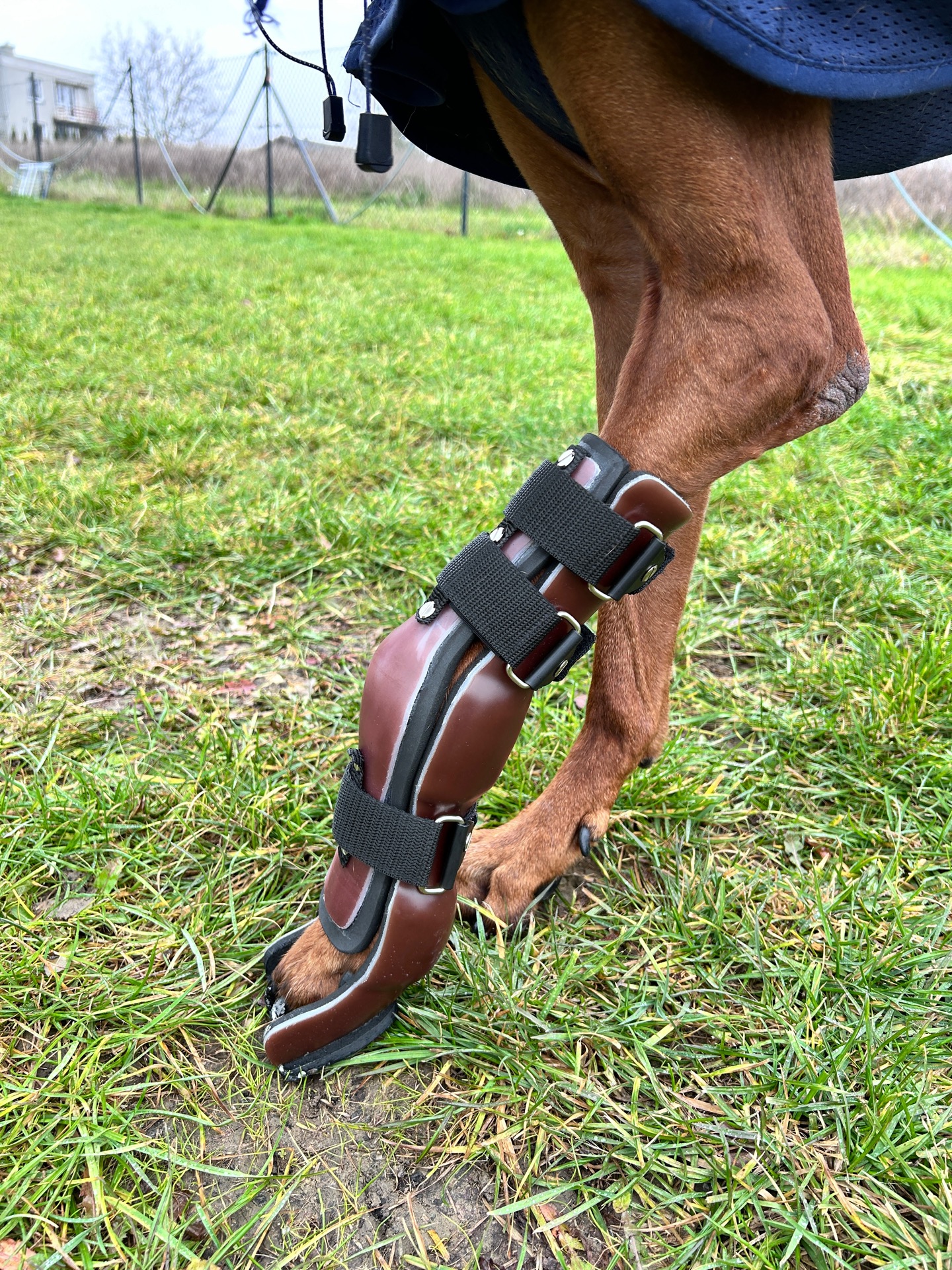
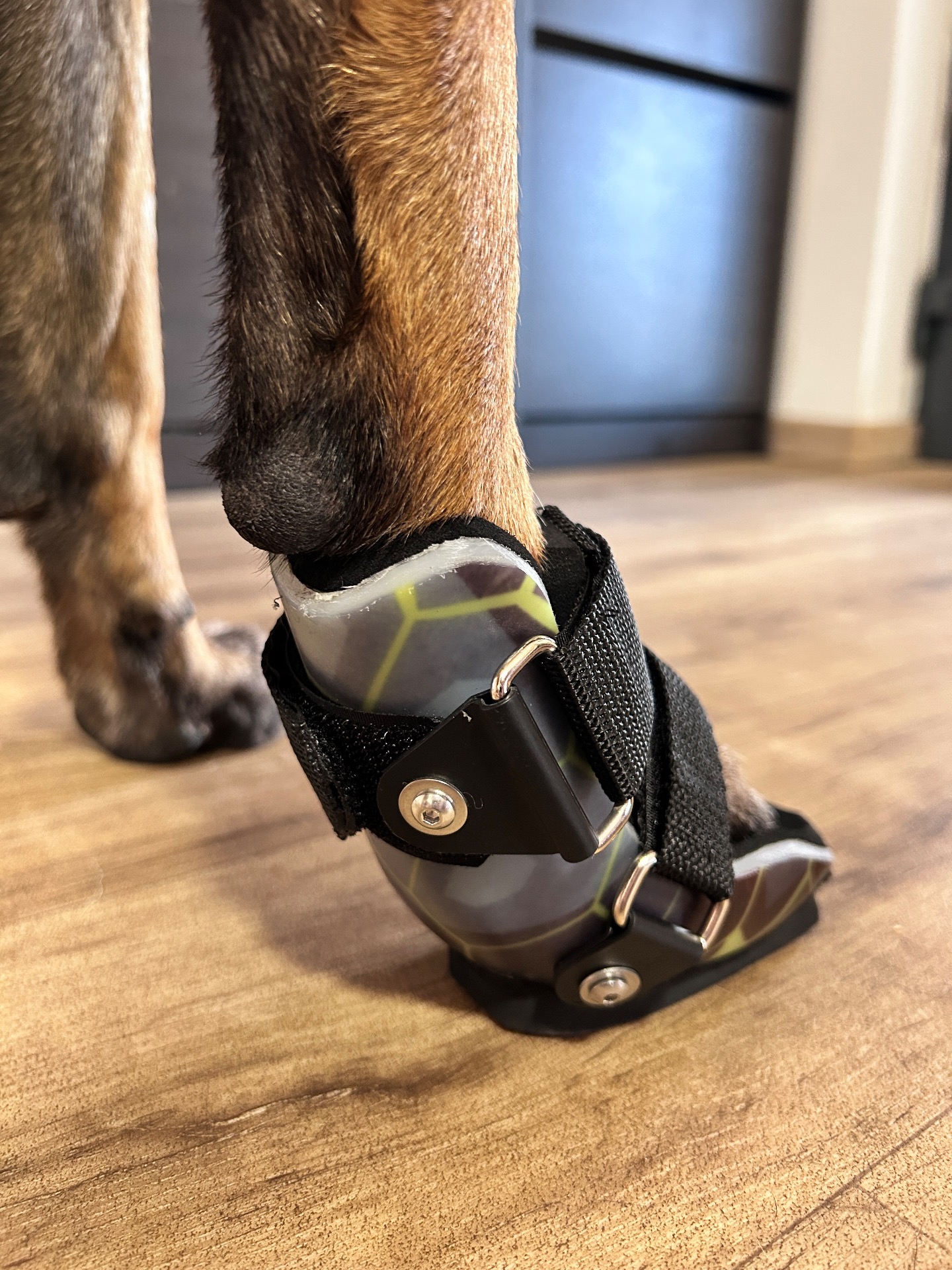
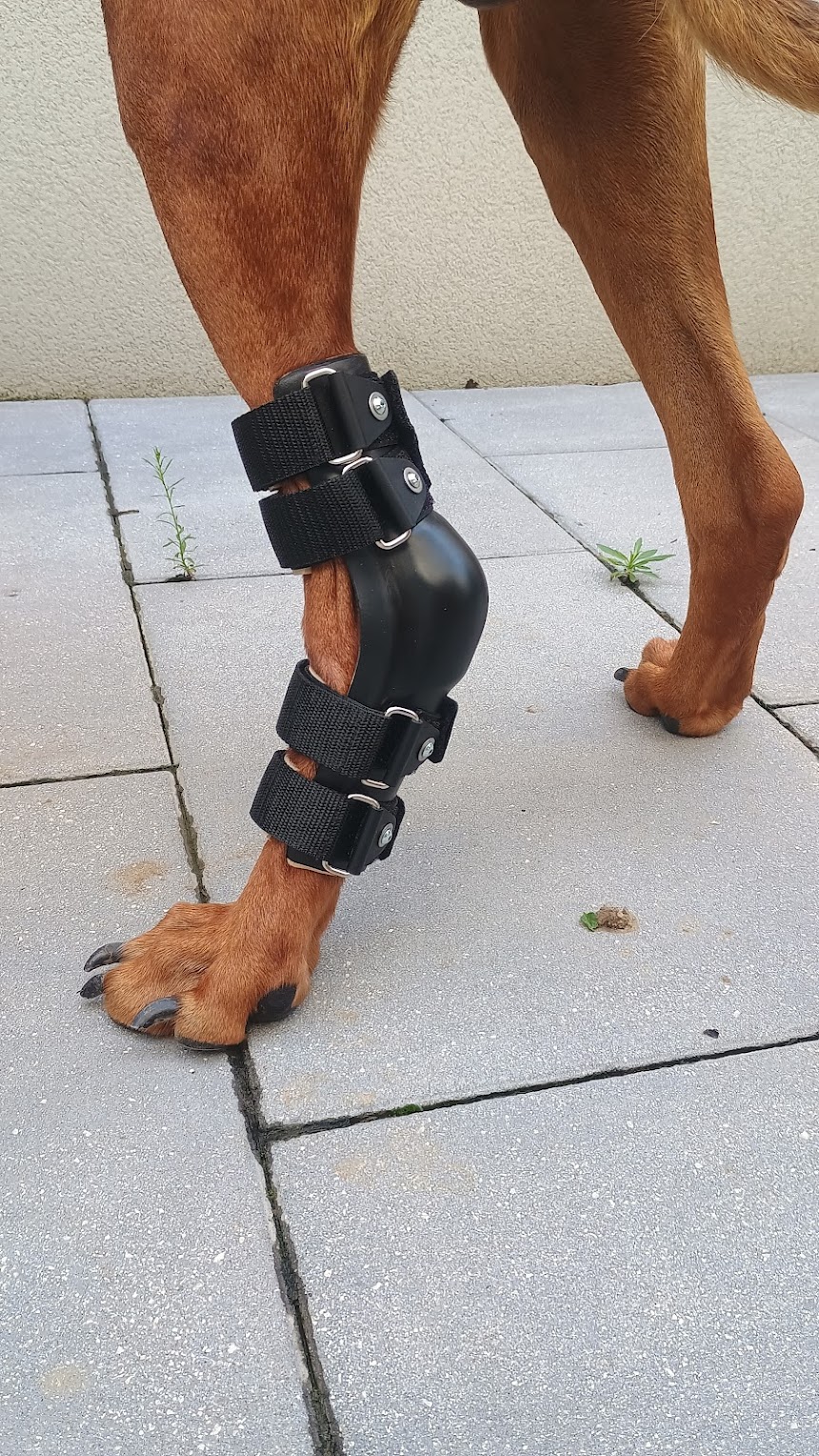
Veterinary orthoses are medical devices specifically designed to support, stabilize, or control motion in a dog's limb or joint affected by injury, instability, or chronic orthopedic conditions. Properly fitted orthoses assist functional movement, reduce compensatory strain, and may complement rehabilitation or surgical planning.
Orthotic Devices by Anatomical Application
Veterinary orthotic devices are designed according to the specific joint or limb segment requiring support. Explore our orthotic solutions based on device type:


Clinical Indications for Canine Orthoses
Orthotic devices for dogs may be considered in the following situations:
joint instability (e.g. ligament injuries such as CCL/ACL deficits)
post-operative stabilization
joint laxity or hyperextension
neurological involvement affecting limb control
chronic conditions requiring biomechanical support
prevention of further joint deterioration
Effective orthotic support is determined by a veterinary assessment, and each case should be individually evaluated.
Clinical Goals of Orthotic Devices
Canine orthoses are intended to:
improve joint stability and controlled motion
support functional weight distribution
reduce compensatory overload on adjacent limbs
assist in gait correction
alleviate pain associated with abnormal joint mechanics
complement physical rehabilitation programs
Orthotic devices are designed to enhance mobility without replacing the limb, focusing on support and stabilization of existing anatomy.
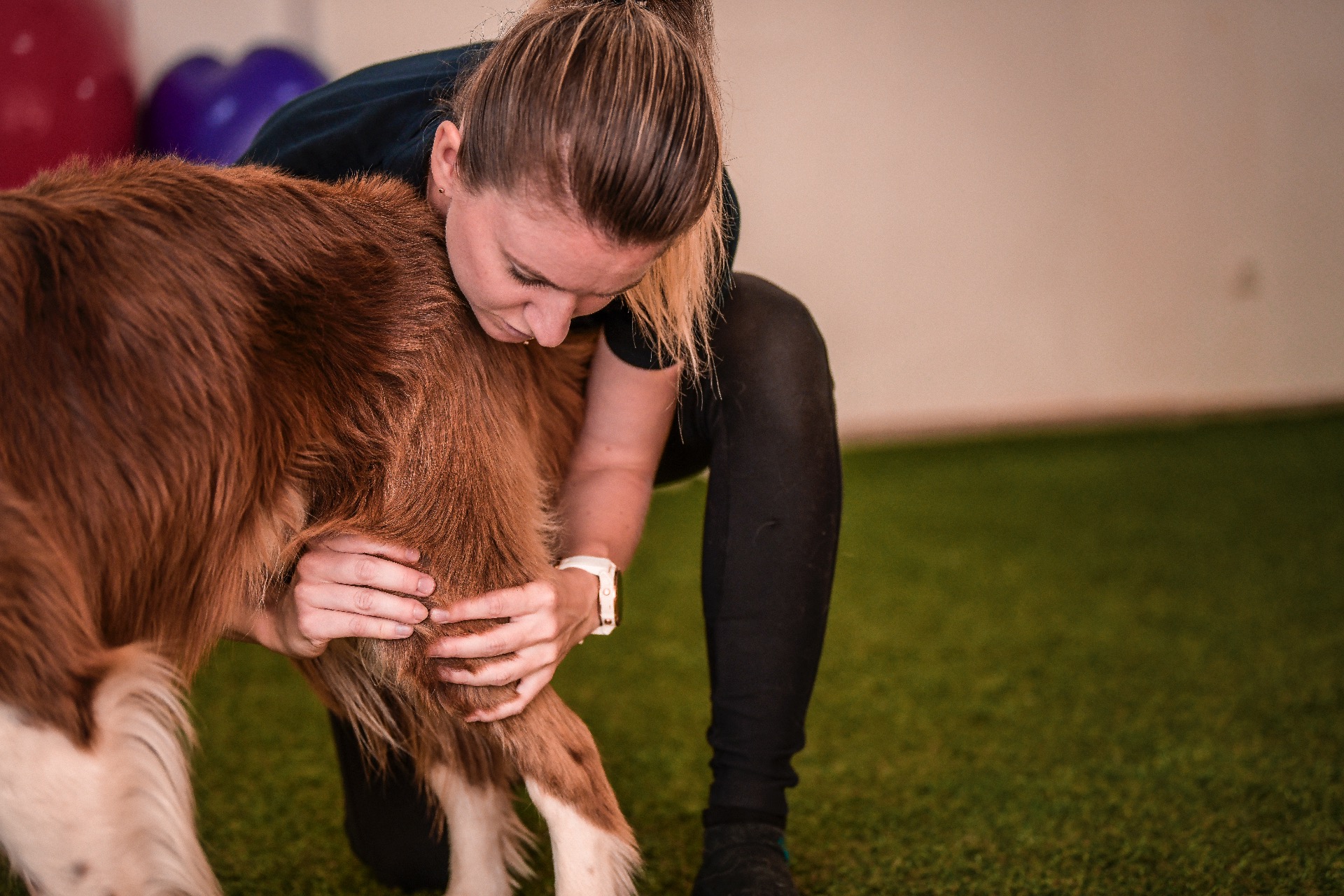

Why Orthoses Require Specialist Expertise
Effective canine orthotic design involves:
understanding joint biomechanics
accurate measurement of limb geometry
assessment of soft tissue tolerance
ensuring controlled range of motion
minimizing pressure points and skin irritation
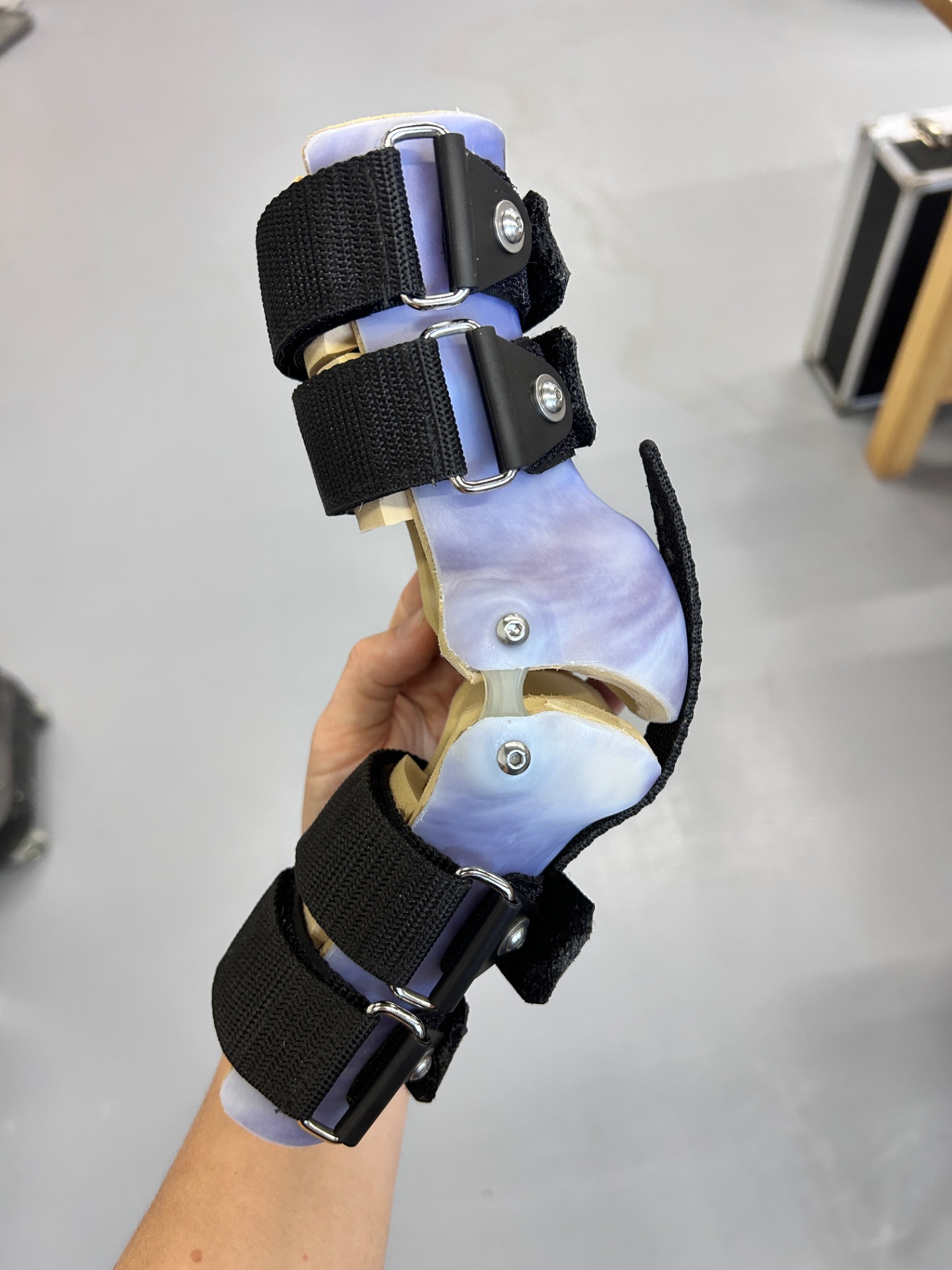
Veterinary orthoses are more than off-the-shelf braces — they must be custom-adapted to each patient's anatomy and functional needs.

Custom Orthotic Design — Tailored for Function
Each orthotic device is developed based on:
detailed veterinary assessment
limb and joint measurements
gait and functional analysis
activity level and lifestyle
specific clinical goals
No two orthoses are identical — each reflects a case-specific biomechanical solution informed by years of experience in complex canine mobility support.
Orthoses vs. Prostheses

Orthoses
- Support and stabilize existing limbs
- Assist controlled motion
- Aid rehabilitation and compensation
- Preserve joint mechanics
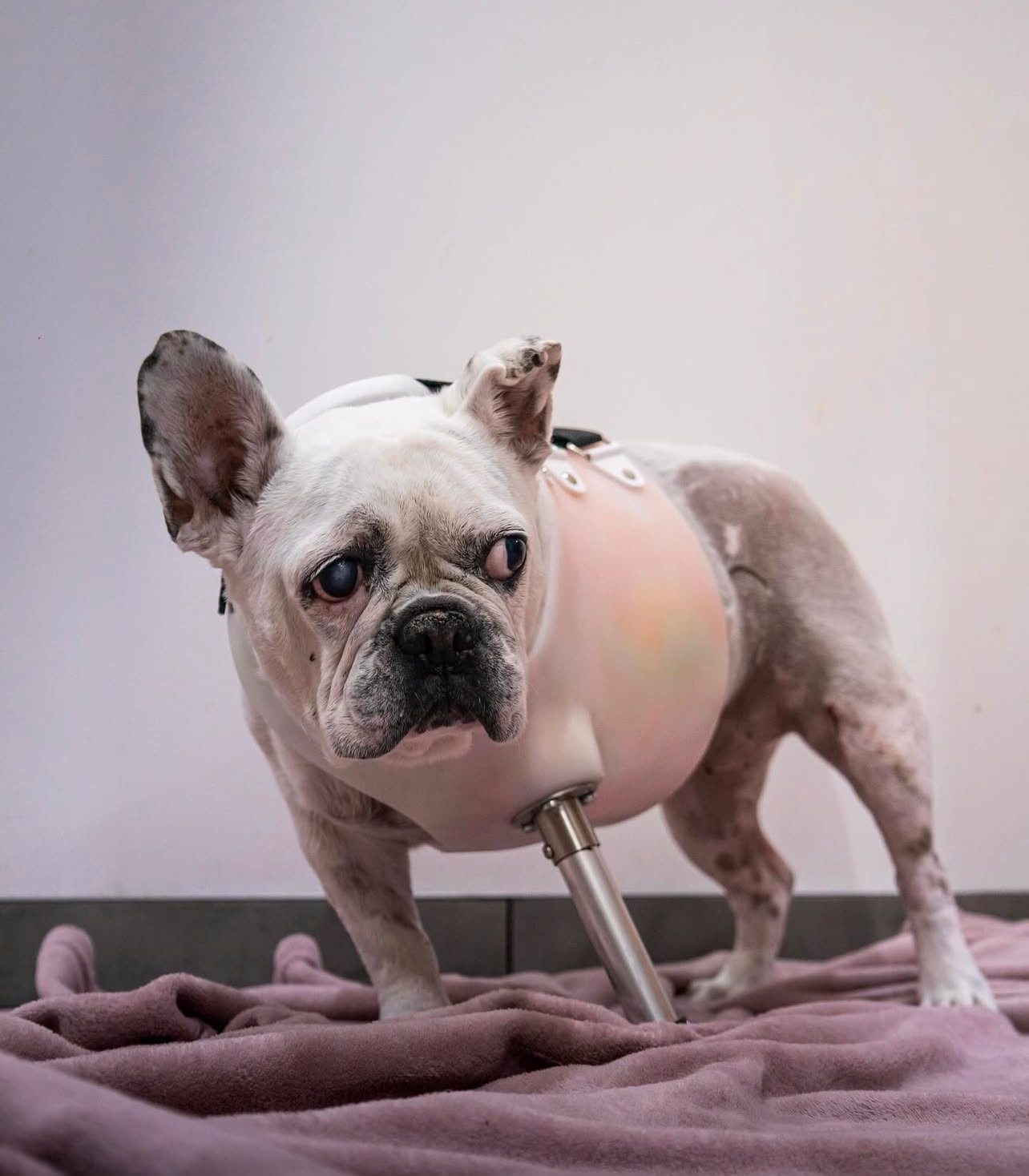

Prostheses
- Replace missing limb segments
- Restore weight-bearing function
- Enable functional replacement
- Provide structural replacement
Choosing the correct device depends on clinical goals, anatomy, and functional needs.
Our Clinical Orthotic Development Process
Veterinary Assessment & Case Review
Diagnostic data, imaging, joint evaluation
Limb Measurement & Biomechanical Analysis
Geometry, alignment, soft tissue tolerance
Custom Design & Fabrication
CAD-based orthotic planning and material selection
Fitting & Functional Testing
Controlled movement assessment and comfort evaluation
Follow-Up Care & Adjustments
Monitoring, progression, and rehabilitation support
Who Can Benefit from Orthotic Devices?
Pet Owners
dogs with ligament instability
dogs in post-surgical recovery
pets with chronic joint laxity
dogs with neurological movement challenges
Veterinary Professionals
diagnostic and rehabilitation planning
orthopedic case support
long-term functional assistance
Discuss the Right Orthotic Solution for Your Dog
Please describe your situation in detail in the message. Additionally, provide information about the animal (species, breed, weight, age), and if possible, also include a photo of the animal.